Industry 4.0 is not only about computers and automation, it applies to Cyber Physical System and Industry Operations. Both Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud computing are necessary in order to progress to Industry 4.0:

Gerald Wong, CEO of Cambridge Industries Group, the company was incepted in 2005 as a boostrapped startup, is in the ICT industry, innovation driven, and R&D intensive.
CIG – Shanghai, China and Santa Clara, CA:
R&D in telecom access products:
– Optical (fiber to the home)
– Wireless (Wi-Fi systems and LTE femtocells)
– Home switches and IoT gateway devices
R&D in manufacturing technologies:
– Industry Information Technologies
– Industry Automation Technologies
He highlighted the four driving forces for the Evolution to Industry 4.0.
- Strategic Directions: Industry 4.0, Manufacture 2025, etc.
- Innovations and Technologies: Automation Technologies, Industry Information Technologies, Other Advanced Technologies, etc.
- Operational and Practical: Staying Competitive, Overcoming Cost Challenges, Overcoming Labor Challenges, etc.
- The Profound Impact on the Future: Corporate Social Responsibilities, People’s Desires for Quality of Life and Quality of Work, etc.
In the internet era, the competition between countries and companies continue to become more intense, competing on various kinds of costs and overall efficiency. The desire for “Mass Customization” may arise, as high manufacturing agility and flexibility are required. Labour issues may happen, robots may replace some human jobs, unemployment rate may increase eventually.
For example, the labour costs in Shanghai increased 110% in the last 8 years, industry 4.0 can reduce the variable costs for factories while fix costs is required for installation of machineries. This is attractive as factories are willing to have a higher net profit in future financial statements.
In Industry 4.0, we have:
– Autonomous Robots, Automation integrated
– CPS – IIoT Connected, Wireless Data Acquisition
– Cloud Computing
– Big Data Analytics
– Cyber Security
– Simulation (“Digital Twin”)
– Augmented Reality (VR for manufacturing)
which have a profound impact, as the new industry revolution is unavoidable, efficiency and quality have significantly improved, and so is the positioning for global manufacturing.

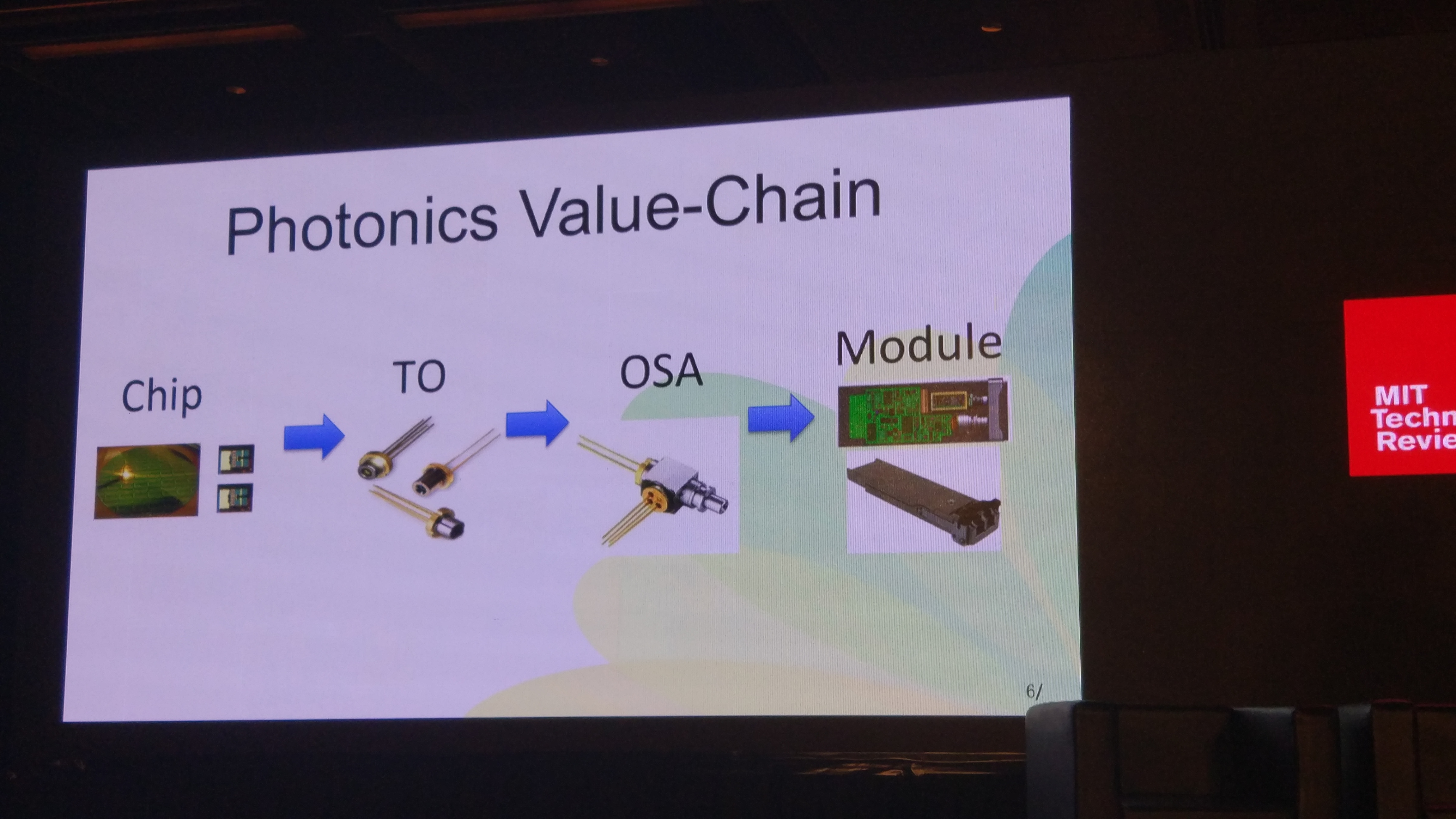
Weiping Huang, the Chairman of Qingdao Hisense Broadband Multimedia Technologies, discussed the progression of microelectronics – transistors’ density have been increasing for the past 40 years. Besides, Vertical Integration Strategy is commonly used by technology companies, he says that many companies involved are in more than one stage of production. His company handles the whole production process, i.e. from Chip to Box. The Photonics Value-Chain contains Chip, TO, OSA, Module, Box, mastering this value-chain can make the production process more efficient with lower production costs.
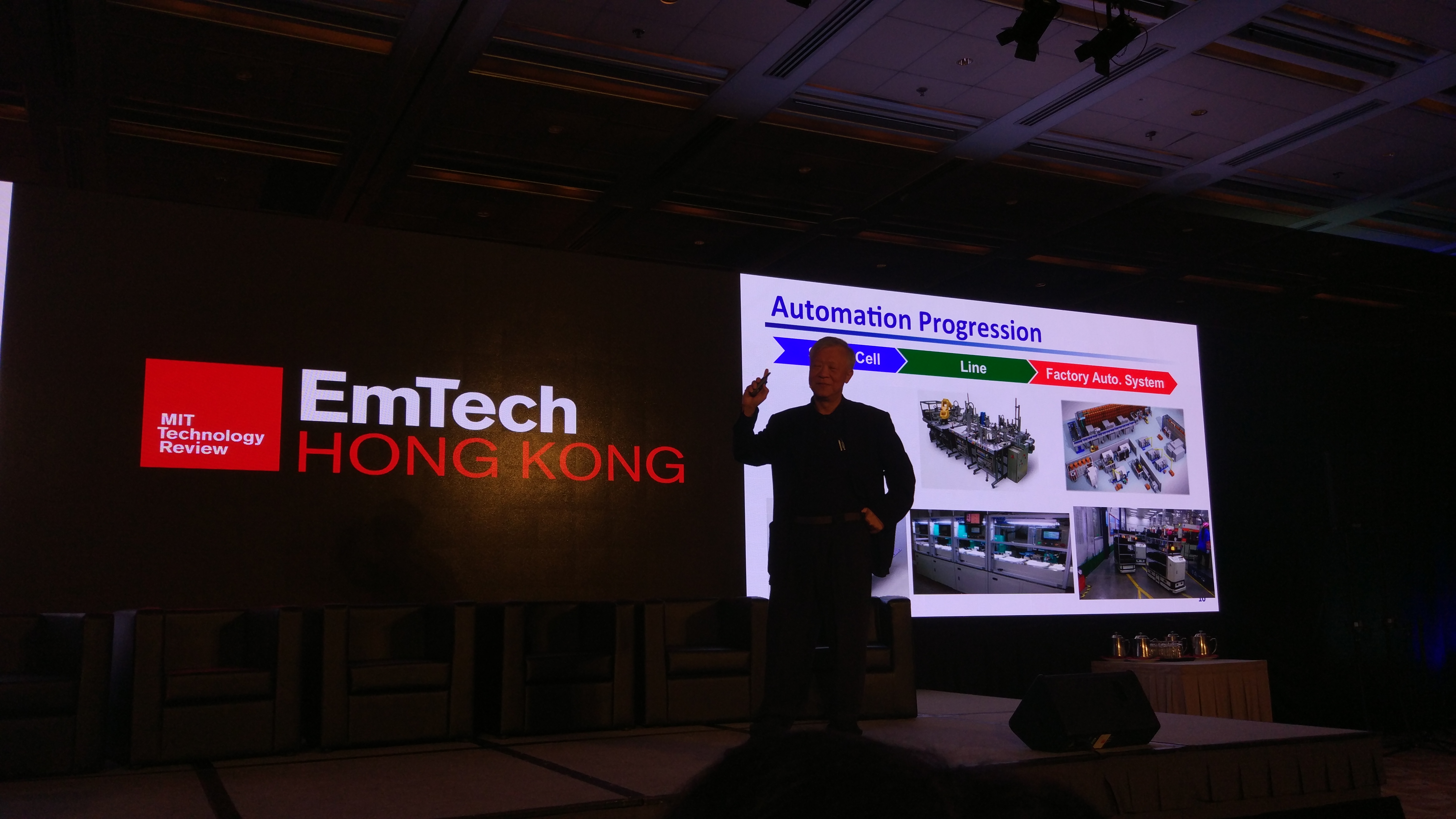
Chia-Peng Day, General Manager of Automation Technology Development Committee, Foxconn, introduced System Integrated Robots for Assembly. The flexible automated assembly line is combined by a family of small robots, Integrated machine vision, Smart tools & grippers for small parts assembly, Precision Parts feeders & fixtures and Precision workpiece transport platform. China is progressing towards a new initiative – “Made in China 2025” – transforming the country into an advanced manufacturing powerhouse, it requires fast development in three major technologies: Cloud, Big Data and IoT.

Duncan Turner, Managing Director of HAX states that Shenzhen is a good place for technology innovation as the place has a large talent pool of engineers. Besides, he also mentioned that technology is embedded everywhere, the new trend for wearable devices is that they are capable of detecting body movements.